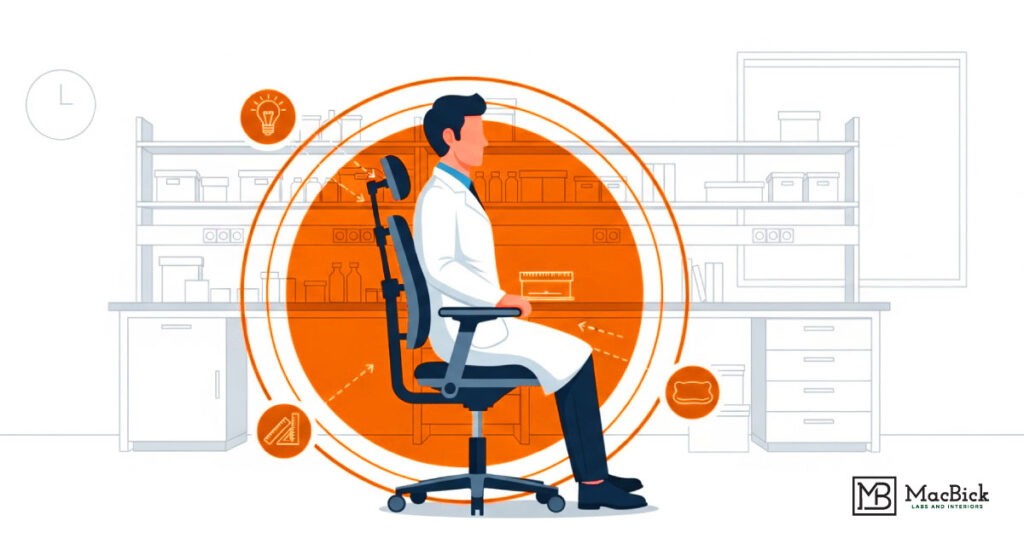
Laboratory spaces require high levels of hand-eye coordination and constant arm and hand movements for the manual handling of materials. Performing these activities in traditional laboratory environments often leads to musculoskeletal disorders and cumulative trauma injuries among researchers and scientists.
This is where ergonomic principles come into play and highlight their importance. Ergonomic design in labs goes beyond seating—it tailors an environment that meets researchers’ specific needs.
In this blog, we’ll examine various ergonomic considerations in laboratory design and how they create a safe, efficient, and innovative workspace
Understanding Ergonomics in Laboratory Spaces
Ergonomics is about designing workspaces to accommodate scientists’ needs for enhanced comfort and efficiency. It often includes considering factors such as workstation layout, lighting, temperature control, and equipment placement. Laboratory spaces that incorporate ergonomic principles promote a positive work environment and foster creativity, collaboration, and innovation among researchers and scientists.
Why Incorporate Ergonomic Designs in Laboratory Spaces?
Laboratory research often involves extended hours, repetitive tasks, and exposure to potentially hazardous materials. These factors contribute to physical discomfort, fatigue, and even musculoskeletal disorders in researchers and scientists. Implementing ergonomic principles in laboratory design helps mitigate these risks in the working environment. Other reasons for incorporating ergonomic designs in laboratory spaces include:
- Enhanced Comfort and Well-being: Ergonomic chairs in the workstation promote good posture and reduce physical discomfort for researchers and scientists. A comfortable and healthy work environment in laboratories improves scientists’ energy levels and contributes to job satisfaction.
- Increased Productivity: Incorporating ergonomic principles into lab spaces allows researchers to work more efficiently and effectively. It minimizes physical strain and fatigue, leading to increased productivity and improved research outcomes.
- Improved Safety: Ergonomic furniture in laboratories enhances scientists’ balance and coordination. It reduces the risk of accidents and injuries in the lab environment and contributes to a safer, more secure workspace.
- Accessibility and Inclusion: Ergonomic design principles ensure that laboratory spaces are accessible and usable for all researchers, regardless of physical ability.
Key Ergonomic Principles in Lab Design
The key ergonomic principles for creating a safe and comfortable work environment for researchers and scientists help ensure productivity, reduce the risk of injuries, and promote overall well-being. Some of these principles include:
Workstation Design in Labs
Designing lab workstations with ergonomics in mind creates a productive work environment for researchers and scientists.
- Desk and Countertop Height: Proper heights should be maintained to minimize neck and back strain. While seated, elbows should be at a 90-degree angle, and shoulders should remain relaxed.
- Seating: Ergonomic chairs with adjustable height, tilt, and lumbar support help maintain good posture and reduce discomfort. Allowing researchers to customize their seating position minimizes strain on the spine, neck, and shoulders.
- Task Lighting: Adjustable task lighting allows researchers to control light intensity based on specific tasks, minimizing eye strain and fatigue.
Equipment Ergonomics
Proper equipment height and angle are crucial for minimizing neck and back strain. Placing frequently used instruments within easy reach reduces the need for excessive reaching or stretching. Additionally, adjustable equipment stands allow researchers to personalize their viewing position for optimal comfort.
Lighting and Ventilation
Appropriate lighting levels in laboratory spaces ensure optimal visibility and reduce eye strain among scientists. Moreover, adequate ventilation systems help maintain comfortable temperatures in labs.
- Appropriate Lighting Levels: Task lighting, such as desk lamps or microscope lights, should be adjustable to focus light on specific work areas. Ambient lighting provides general illumination throughout the lab, preventing shadows and dark spots.
- Airflow: Consider installing laboratory-specific ventilation systems like fume hoods and biological safety cabinets to manage hazardous materials.
Storage and Organization
Install shelving, cabinets, and drawers at proper heights to optimize workflow efficiency. Adjustable shelving or drawer systems provide flexibility to meet different user needs, improving accessibility and ergonomics in the laboratory setting.
Clutter-Free Workspaces
Efficient layout and organization minimize distractions and optimize workflow in laboratory spaces. Drawer organizers and regular decluttering ensure accessibility and maintain a streamlined workspace conducive to productivity.
Wrapping Up
Prioritizing ergonomic considerations in lab design creates workspaces that promote the well-being and productivity of researchers and scientists. Laboratories can foster a more comfortable and healthy environment by investing in ergonomic solutions.
Ready to revolutionize your lab’s workflow? Apply these ergonomic principles in your lab design and see the difference they make.
Contact MacBick Labs and Interiors now to explore more ergonomic solutions.